Gum Disease
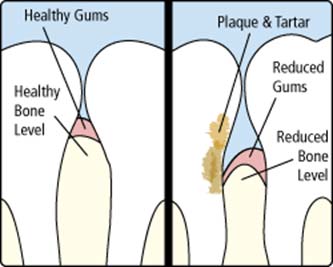
Gum disease, also called periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues surrounding your teeth. In advanced stages, gum disease can lead to sore, bleeding gums, chewing problems, and even tooth loss. In fact, it is one of the primary causes of tooth loss in adults.
What causes gum disease?
Our mouths are always full of bacteria, which constantly form a sticky, colorless “plaque” on surfaces of the teeth. Regular brushing and flossing help eliminate and control plaque buildup, but plaque that is not removed can harden and form “tartar” which cannot be cleaned with brushing. Only a dentist can remove tartar from the teeth.Gum disease creates small pockets that separate the gums from the teeth right below the gum line. There are two stages of gum disease, gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Gingivitis - The early stage of gum disease, which can usually be eliminated by daily brushing and flossing. Gums will become red and swollen and bleed easily.
- Periodontitis - If gingivitis is left untreated, it can advance into periodontitis. Gums and teeth infected at this later stage of gum disease will become irreversibly damaged, as teeth may become loose, fall out, or require extraction by a dentist.
Certain factors can increase a patient’s risk of developing gum disease, including:
- Smoking
- Chewing tobacco
- Hormonal changes
- Diabetes
- Crooked teeth
- Old fillings
- Pregnancy
- Medications that lessen the flow of saliva
- Certain types of medication such as steroids, anti-epilepsy drugs, cancer therapy drugs, calcium channel blockers, and oral contraceptives
Symptoms of gum disease include:
- Bad breath that won’t go away or an unpleasant taste in the mouth
- Red, swollen, tender, or bleeding gums
- Painful chewing
- Pus between the teeth and gums
- Loose or sensitive permanent teeth
- Receding gums or longer appearing teeth
- Change in the way the teeth fit together when you bite
Treating Gum Disease
The main goal of gum disease treatment is to control the infection. The type of treatment will vary, depending on the extent of the gum disease. Standard treatment options include:- Non-surgical treatments such as at-home periodontal trays, scaling, and root planning (deep cleaning)
- Periodontal surgery and laser gum surgery
- Dental implants